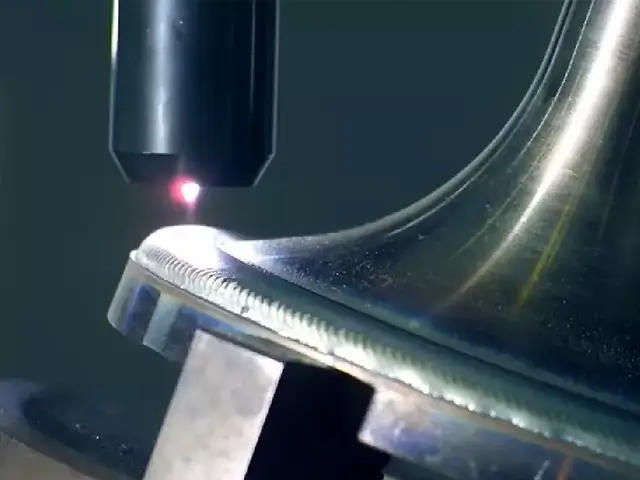
advantages of laser cladding
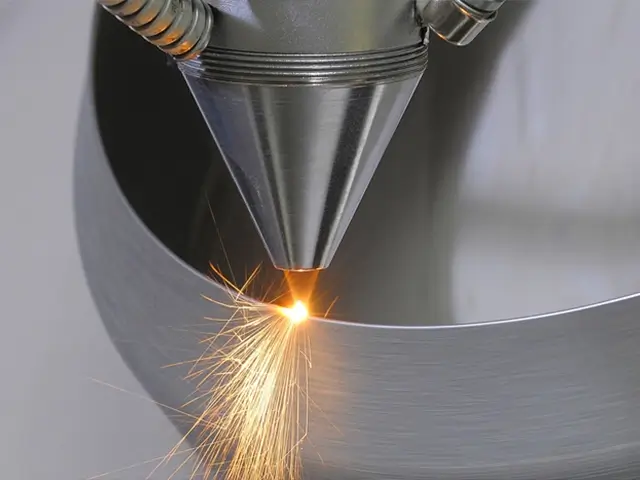

Precise Material Deposition
Laser cladding provides highly controlled deposition of material, allowing for precise coating thickness and minimal material waste. This precision ensures high-quality results for applications that require detailed surface repairs or enhancements.
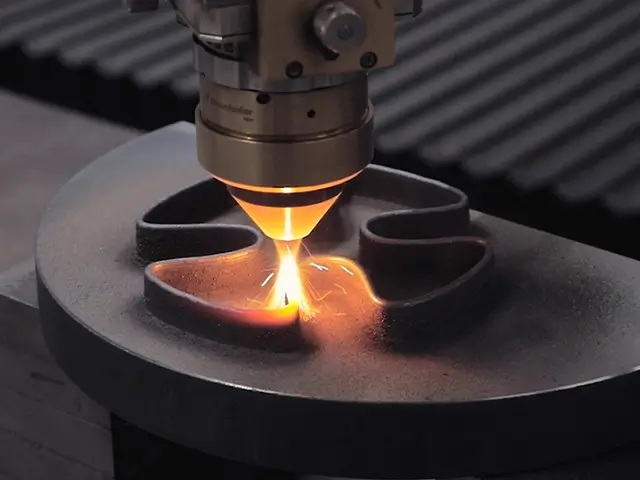

Minimal Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ)
Laser cladding generates a localized heat zone, reducing thermal distortion and preserving the properties of the base material. This minimizes material stress and potential warping, particularly on sensitive components.
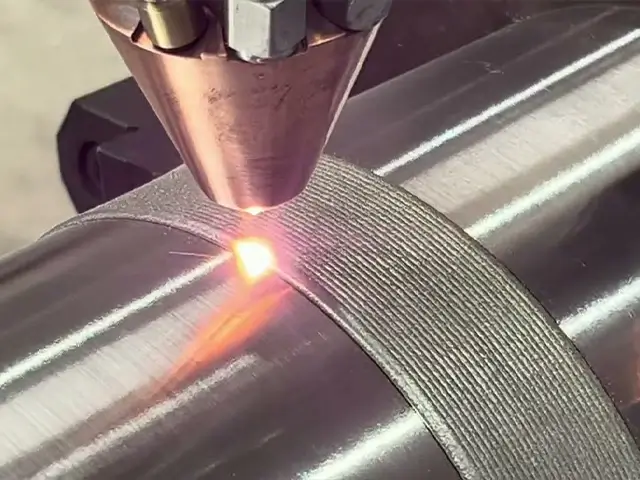

Enhanced Surface Properties
Laser cladding improves the wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and hardness of the base material, extending the lifespan of components. It is commonly used to restore or enhance the performance of high-wear industrial parts.
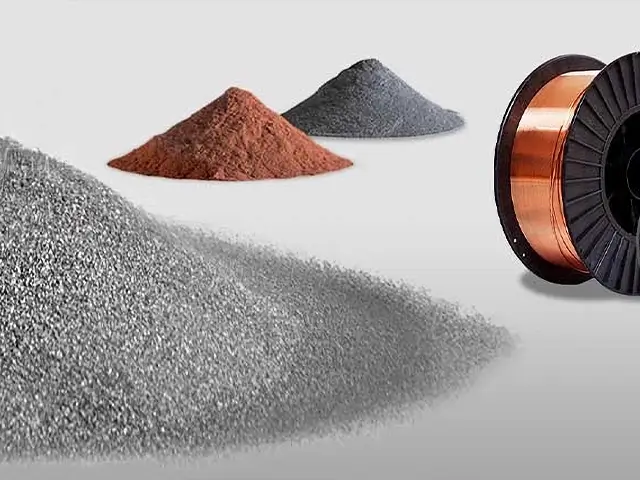

Versatile Material Compatibility
It allows for the deposition of a wide range of materials, including metals, alloys, and ceramics, onto various substrates. This versatility makes laser cladding suitable for a broad spectrum of industries such as aerospace, automotive, and oil & gas.
types of laser cladding
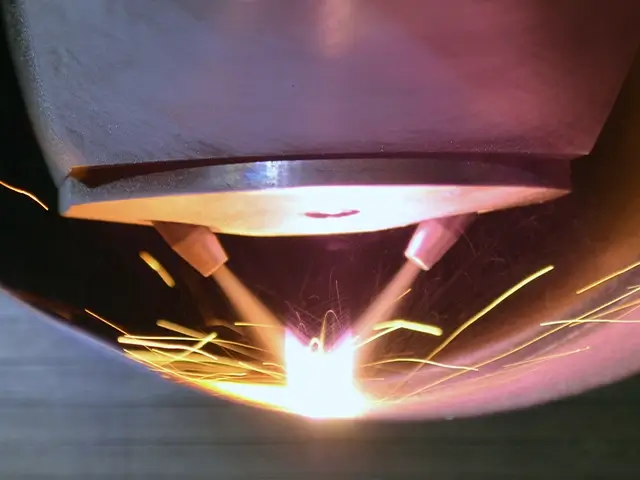

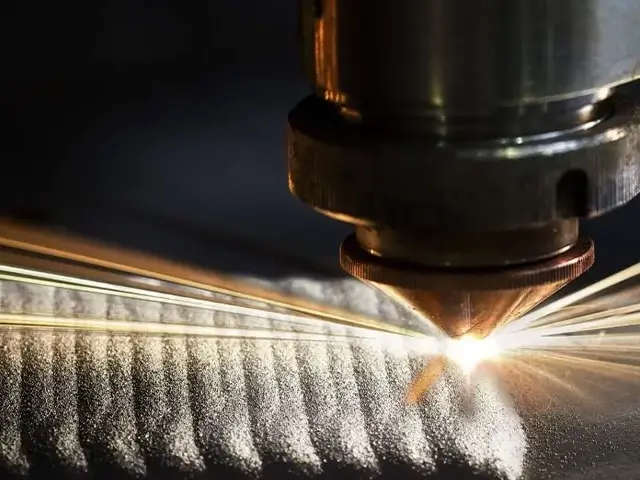
Blown Powder Laser Cladding
In this method, powdered material is blown through a nozzle into the laser beam and then onto the substrate where it is melted to form a coating. It is the most common laser cladding technique due to its precision and flexibility.
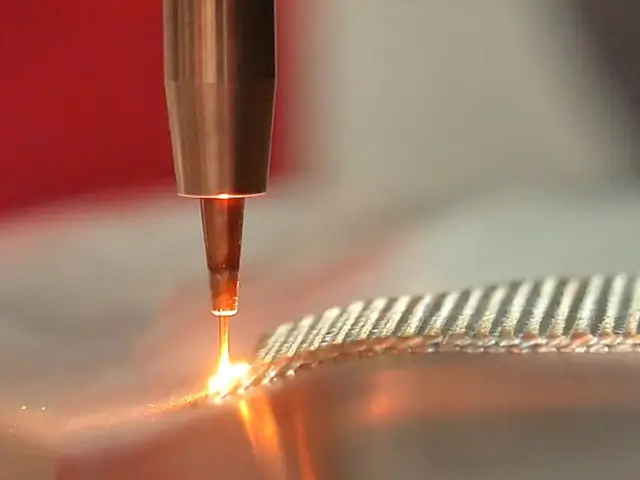

Wire Feed Laser Cladding
In wire feed cladding, a metal wire is fed into the laser beam and melted onto the surface. This method is often used for high-volume applications due to its efficiency and material deposition rate.

Pre-Placed Powder Laser Cladding
The powder material is pre-placed onto the substrate before the laser is applied, melting the material and bonding it to the surface. This method is suitable for large-area cladding and specific applications requiring thick coatings.
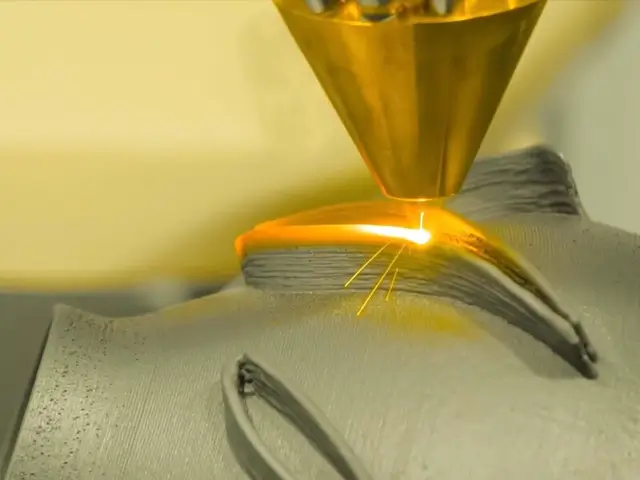

Direct Energy Deposition (DED)
A more advanced form of laser cladding, where powder or wire material is simultaneously deposited and melted by the laser beam. It is often used for additive manufacturing, including repairing or building up parts layer by layer.
laser vs alternate
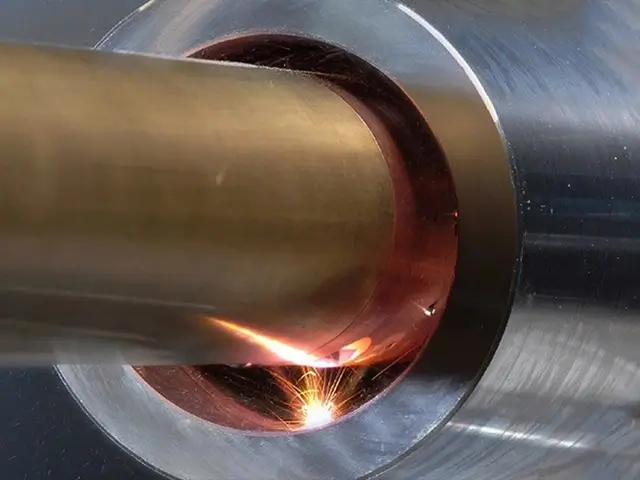

laser cladding
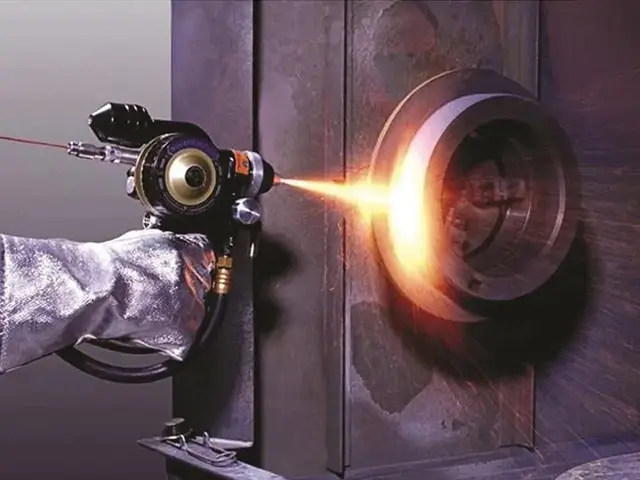

Thermal Spraying
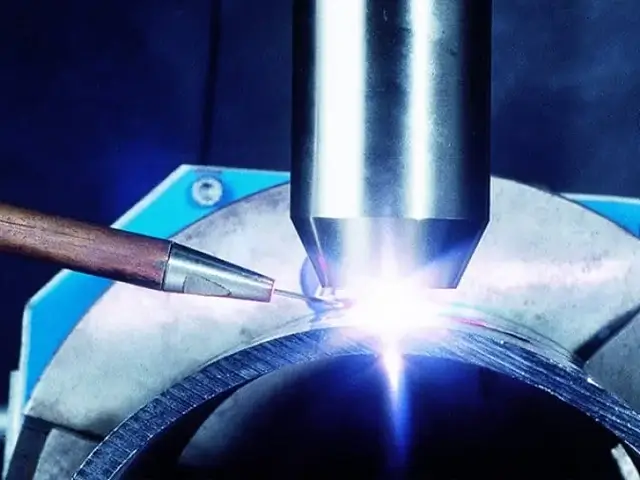
Plasma Transferred Arc (PTA) Welding