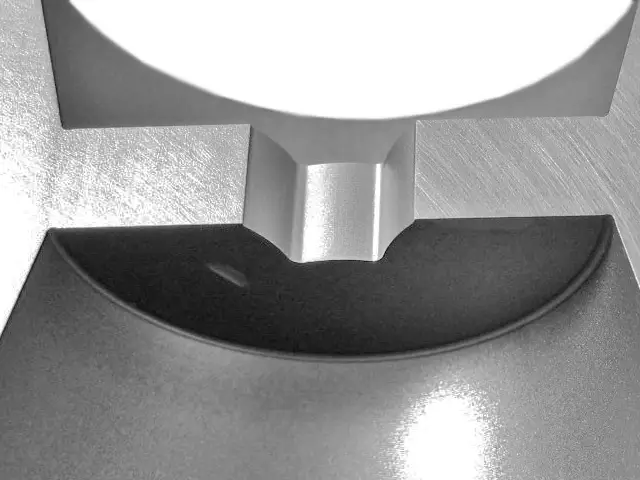
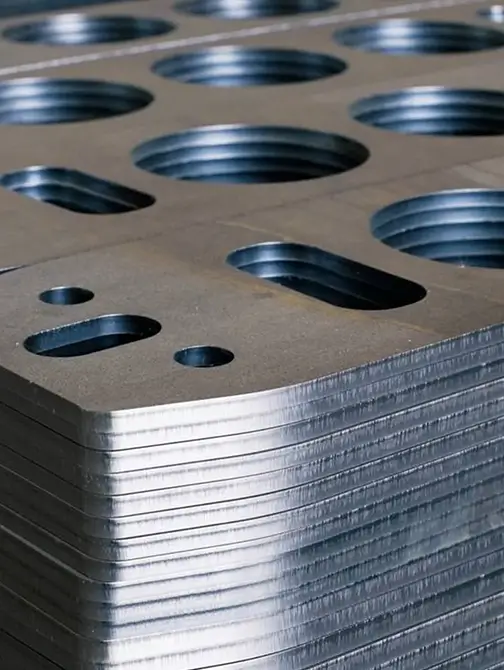
Laser Cutting Technology
advantages of laser Cutting
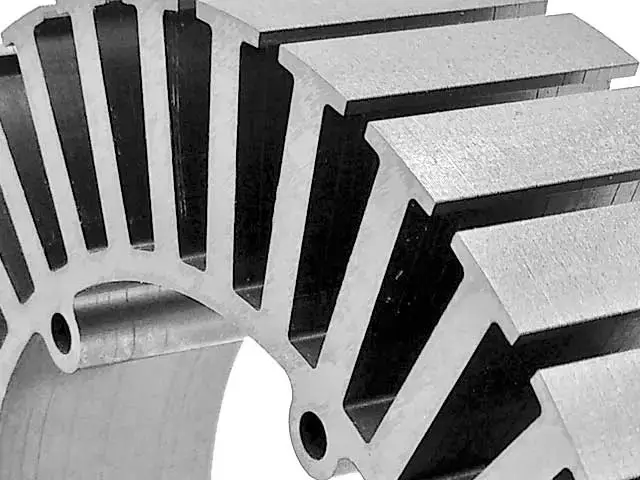

High Precision and Accuracy
Laser cutting allows for extremely precise cuts with tight tolerances, enabling complex designs and intricate details that are difficult to achieve with traditional cutting methods.
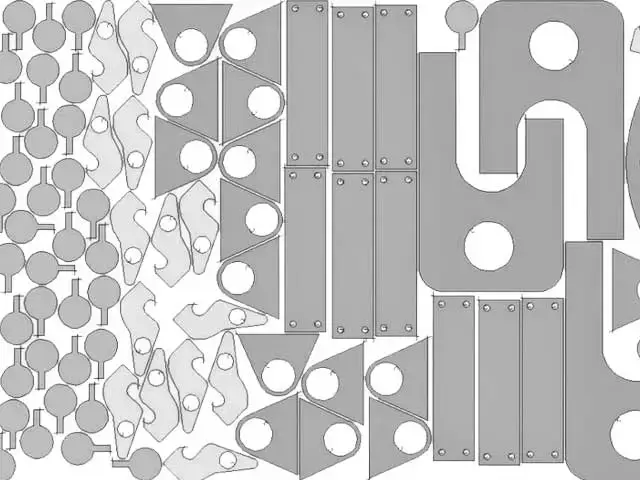
low wastage & cost saving
The focused laser beam reduces material waste by producing narrow kerf widths, maximizing the use of raw materials and lowering production costs.
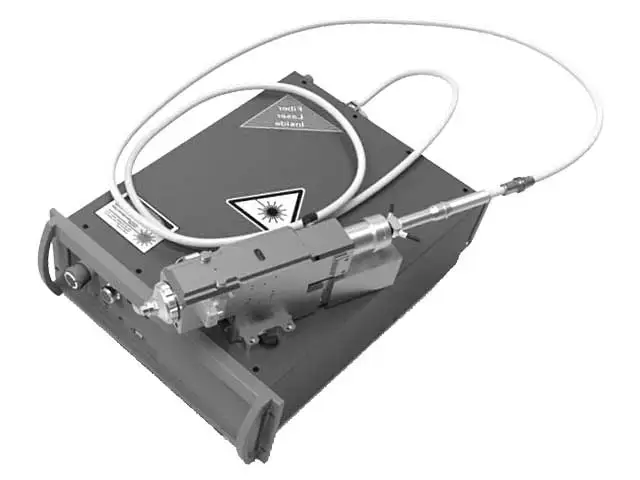
EXTREMELY FLEXIBLE
Laser cutting can handle a wide variety of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, and ceramics, making it suitable for diverse applications across multiple industries.
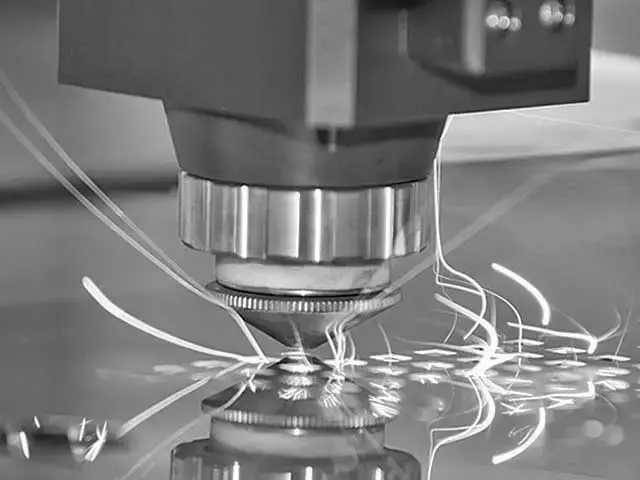

Faster Cutting Speeds
Compared to conventional cutting techniques, laser cutting operates at higher speeds, increasing production efficiency and reducing turnaround times, especially in high-volume manufacturing.
types of laser Cutting
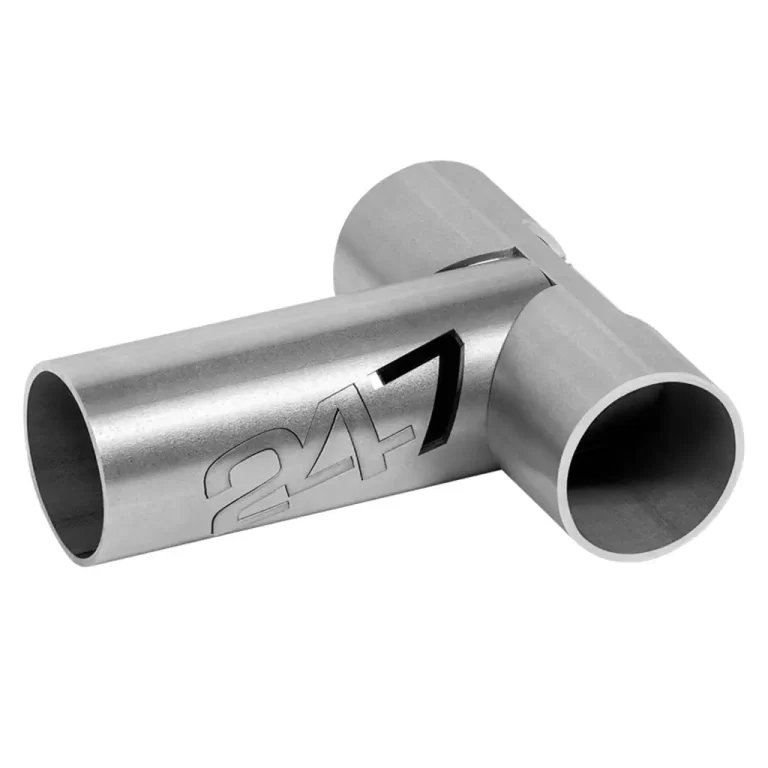

Fusion Cutting
In fusion cutting, the laser melts the material, and an assist gas (typically nitrogen or argon) is used to blow the molten material away from the cut. This method is used for materials like stainless steel and aluminum, where oxidation needs to be minimized.
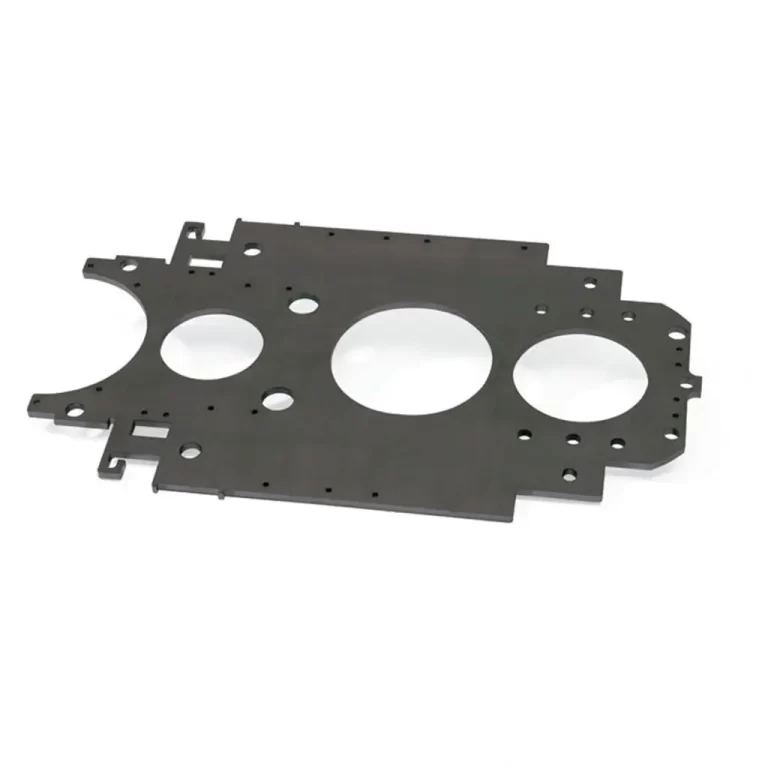

Flame Cutting
This process uses oxygen as the assist gas. The laser heats the material to ignition, and the oxygen assists by creating an exothermic reaction that helps cut through thicker materials like carbon steel.
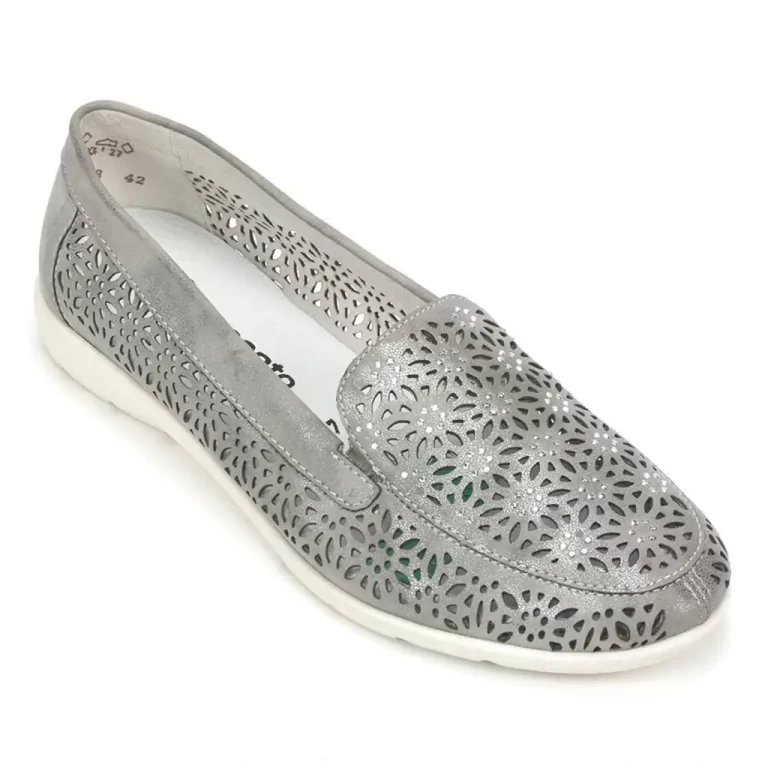

Vaporization Cutting
In vaporization cutting, the laser beam heats the material to its boiling point, causing it to vaporize and create a cut. This method is ideal for materials like wood, plastic, and certain metals where material removal by vaporization is desired.
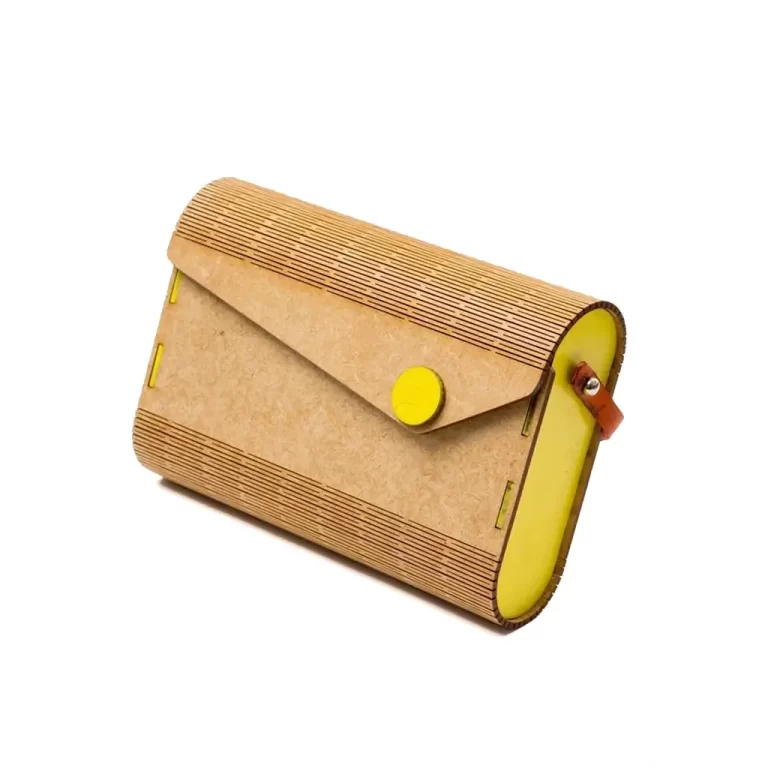

Sublimation Cutting
Similar to vaporization, sublimation cutting involves turning solid materials directly into gas using the laser’s heat without passing through a liquid phase. This method is common in cutting materials like paper, textiles, and polymers.
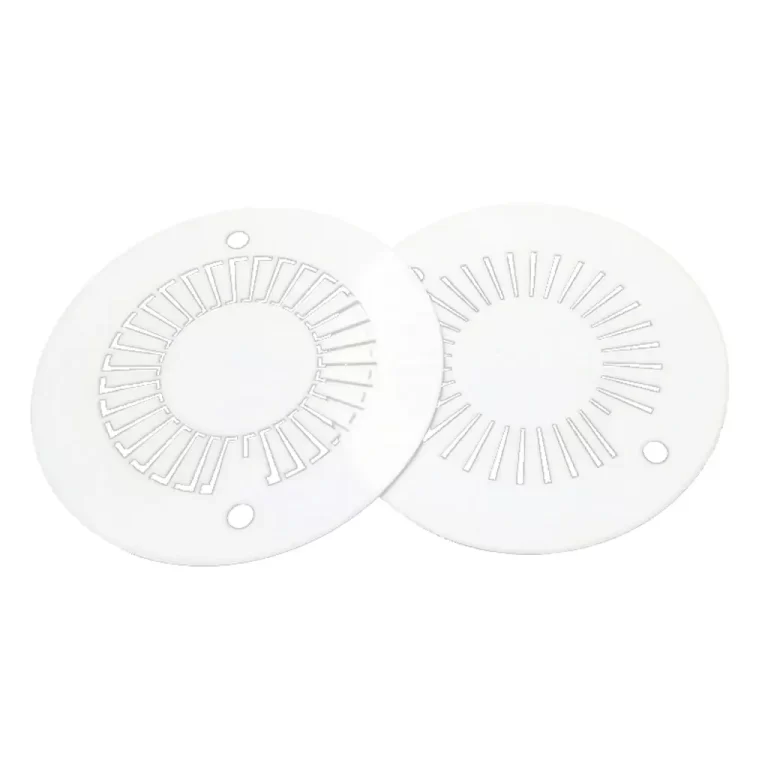

Thermal Stress Cracking
Used for cutting brittle materials like glass or ceramics, this method uses the laser to heat the material, creating a thermal gradient that causes controlled cracking along a precise path.
laser vs alternate

Laser Cutting

Plasma cutting

Waterjet cutting

