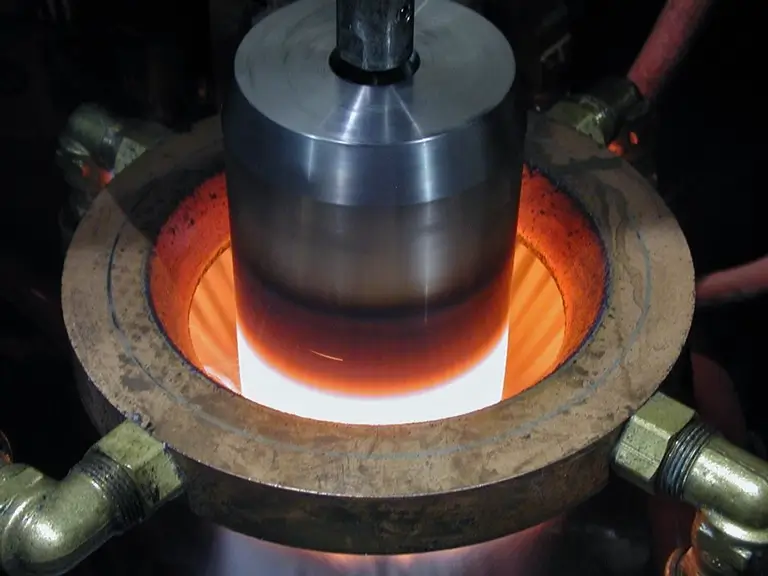
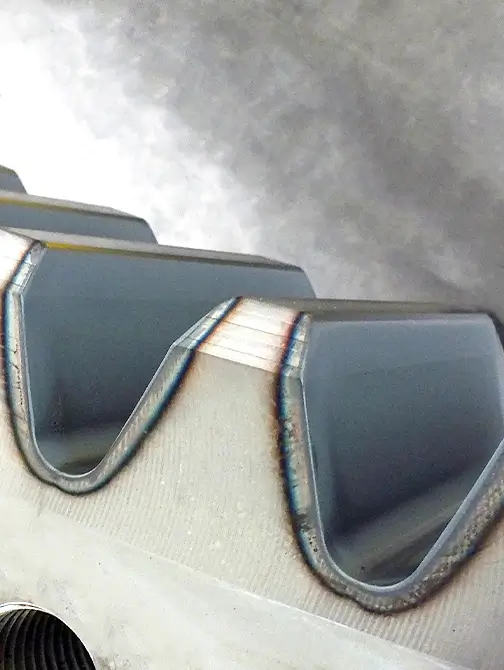
advantages of laser Hardening
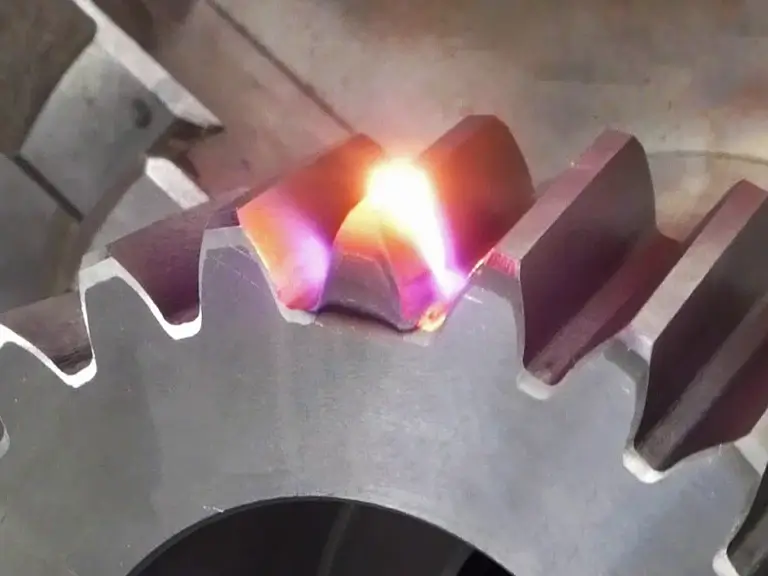

Precise Control
Laser hardening offers highly controlled heat treatment, allowing precise targeting of specific areas of the material. This results in localized hardening without affecting the entire workpiece, making it ideal for complex or delicate components.
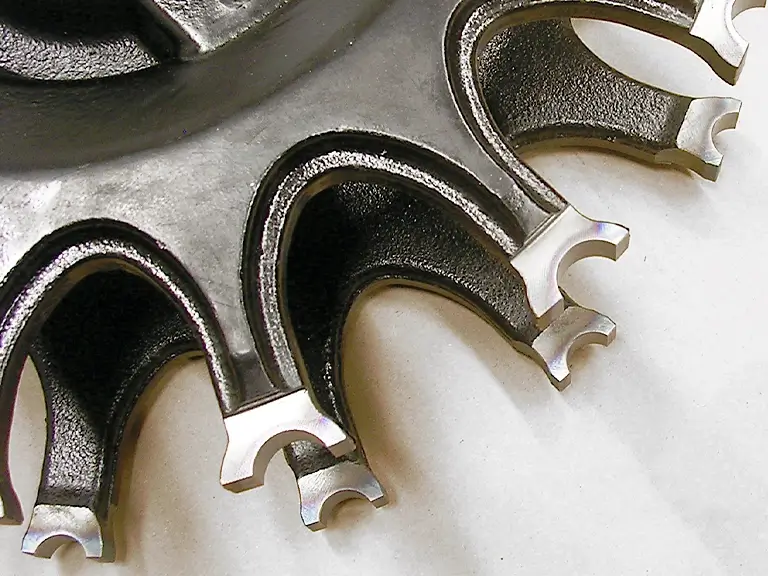

Minimal Distortion
Due to its focused heat application, laser hardening minimizes thermal distortion, reducing the risk of warping or cracking compared to traditional heat treatment methods.
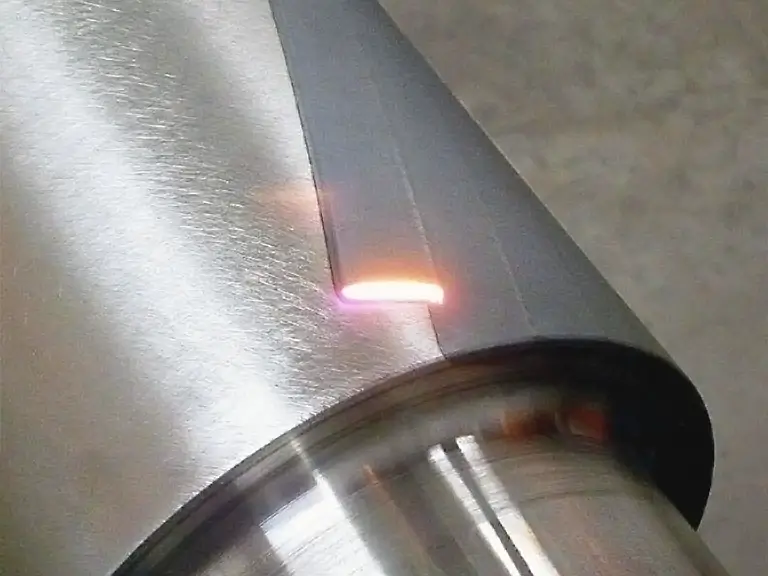

High Surface Quality
The process creates a smooth and hardened surface without the need for additional grinding or finishing, saving time and ensuring uniform hardness across the treated area.
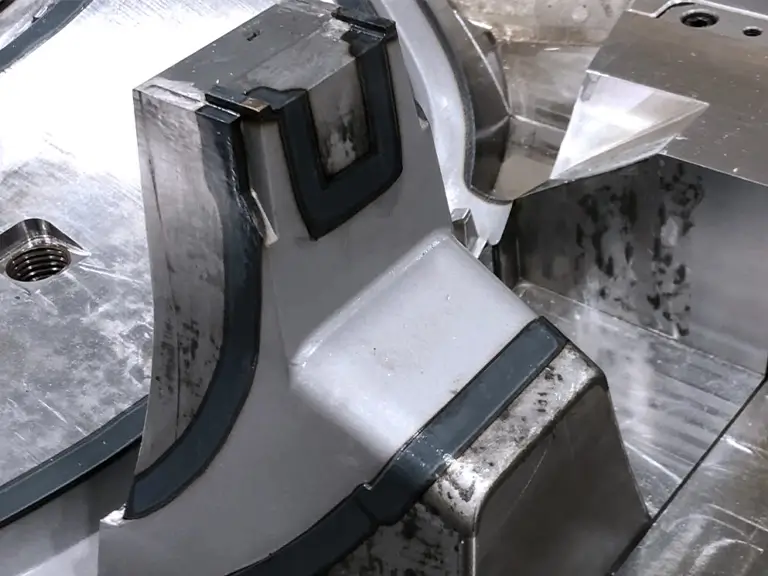

Energy Efficient Fast Process
Laser hardening is a fast process that requires less energy than conventional methods. It also eliminates the need for quenching, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
types of laser Hardening
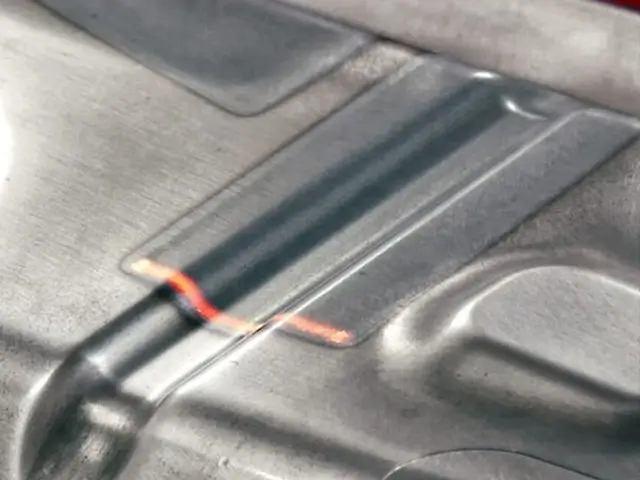

Surface Hardening
A laser is used to heat the surface of the metal to a precise depth, transforming the structure to create a hardened surface layer. This is commonly used in automotive, aerospace, and tool-making industries.
Selective Hardening
Only specific areas of the component are hardened using a laser. This method is ideal for parts that need different hardness levels in different zones, such as gear teeth or cutting edges.
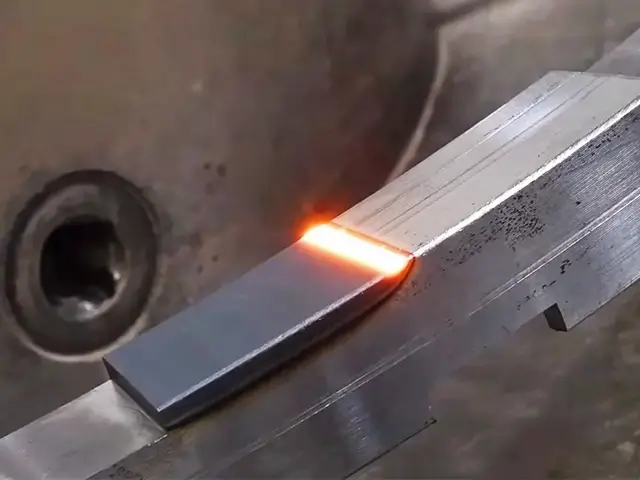

Quench and Temper
In this method, the laser heats the material, and the natural cooling effect results in self-quenching. This leads to hardening without the need for external cooling fluids.
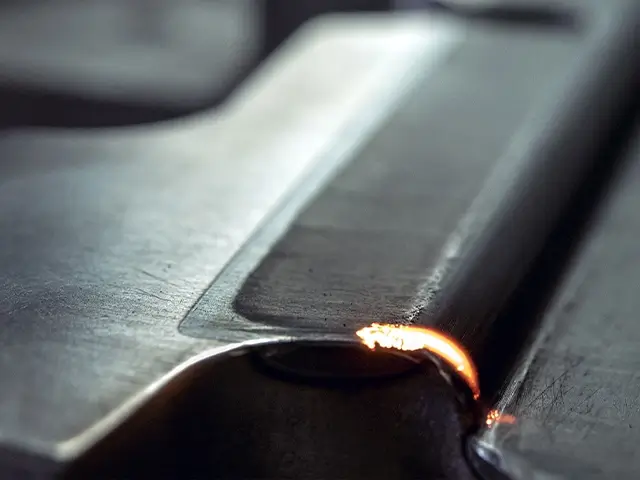

Transformation Hardening
In this process, the laser alters the crystalline structure of the surface to increase hardness through a martensitic transformation, often used for steel parts.
laser vs alternate
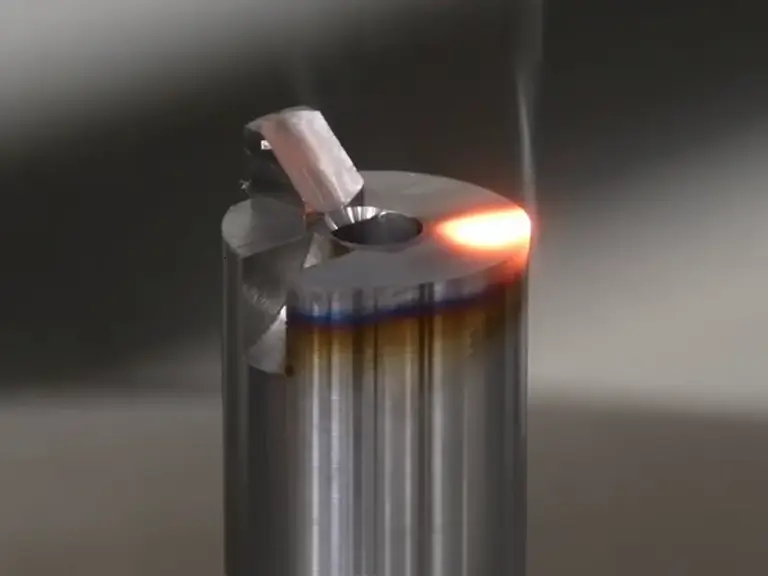

laser Hardening
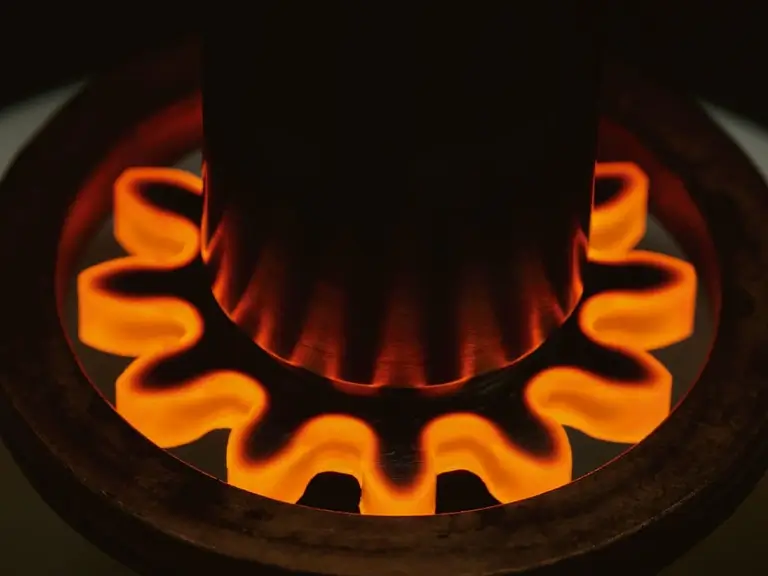

Induction hardening
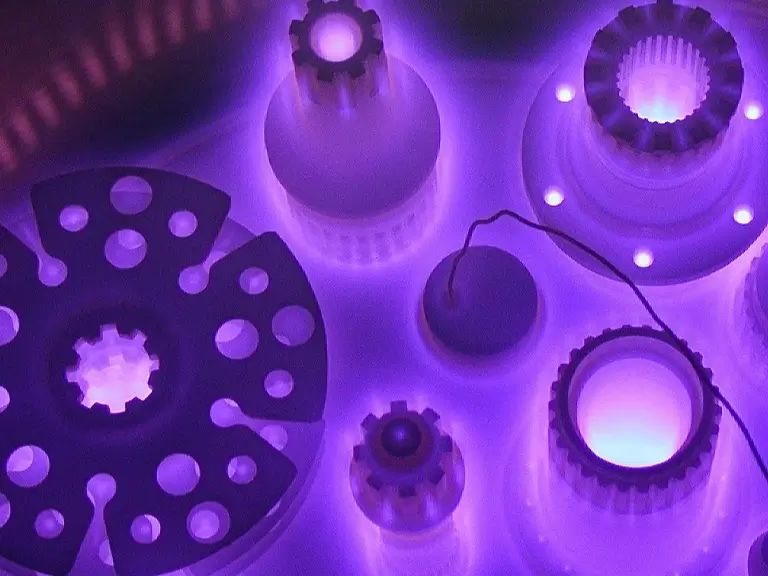

nitriding

