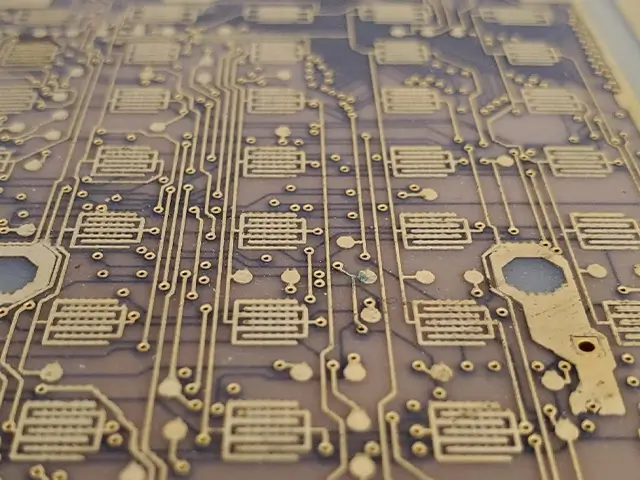
advantages of laser Scribing
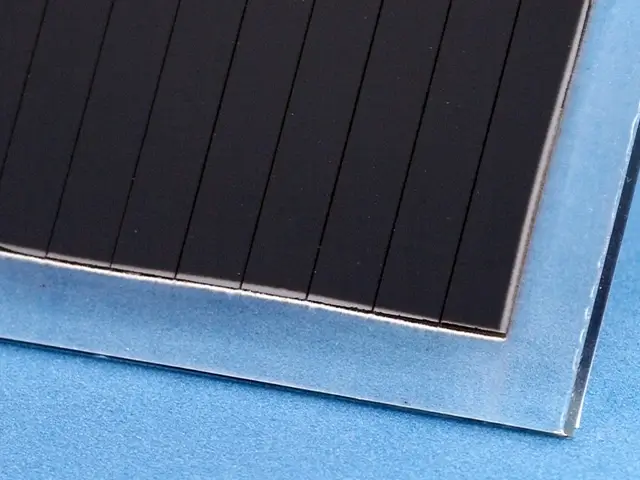

Non-Contact Process
The laser beam does not physically touch the material, reducing the risk of mechanical damage or contamination, which is especially useful for delicate or sensitive materials.

High Precision and Accuracy
Laser scribing allows for extremely precise cuts and markings, enabling detailed and intricate designs on a wide variety of materials with minimal waste.
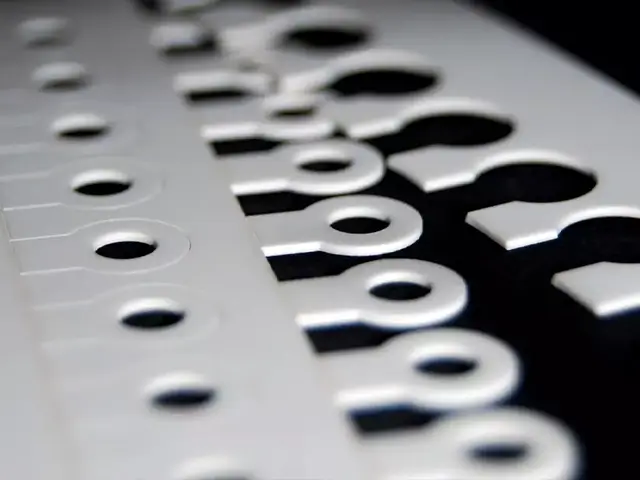

Minimal Material Waste
Laser scribing produces clean cuts with minimal kerf width, resulting in less material waste compared to mechanical methods.
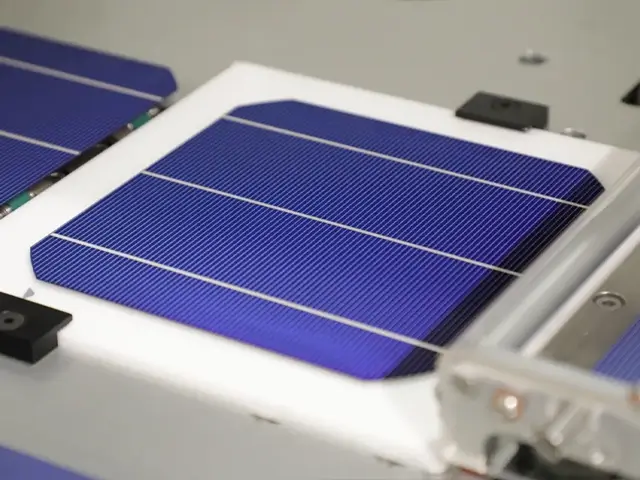
Versitality
Laser scribing can be used on a wide range of materials, including metals, ceramics, glass, and semiconductors, making it adaptable for various industries such as electronics, automotive, and solar panels.
types of laser Scribing
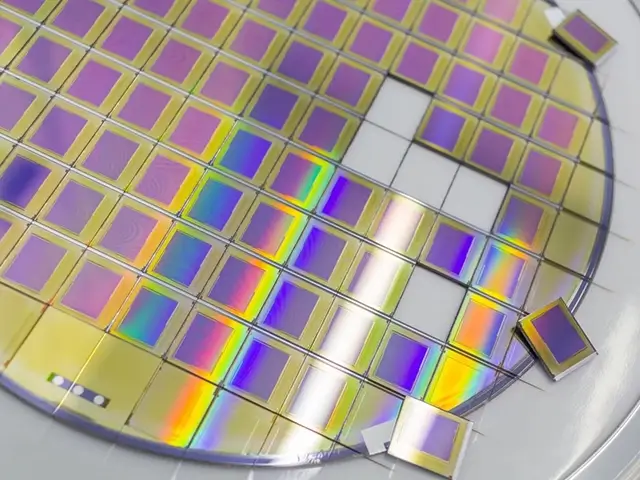
Thermal Laser Scribing
In this process, the laser heats the material to create thermal stress, which causes micro-cracks that guide the scribing line. This method is often used on brittle materials like glass or ceramics.
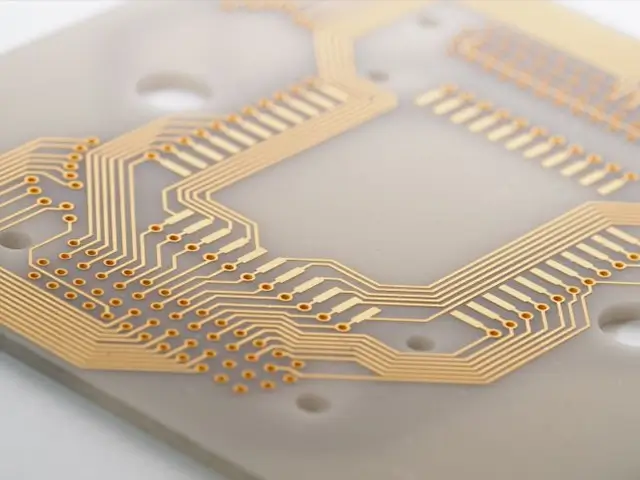
Ablative Laser Scribing
Ablative scribing removes material layer by layer with the laser, vaporizing or ablating it away to form a precise scribe. This method is commonly used in applications such as semiconductors, solar cells, and thin-film materials.
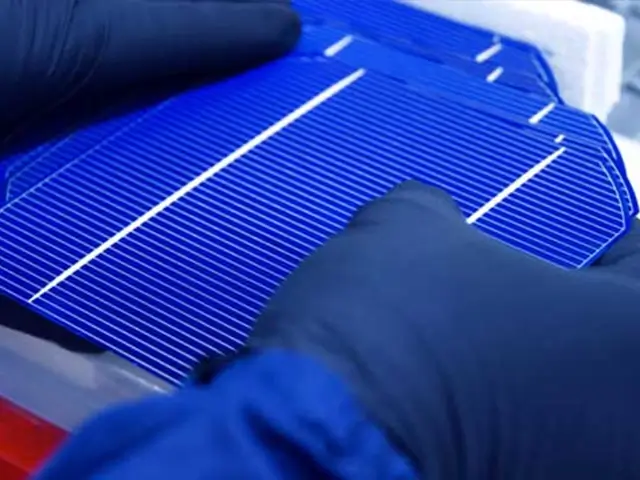

Continuous Wave Laser Scribing
A continuous laser beam is used to scribe materials in a steady stream, providing deep and continuous cuts. This method is suitable for thicker materials and applications where uninterrupted lines are required.
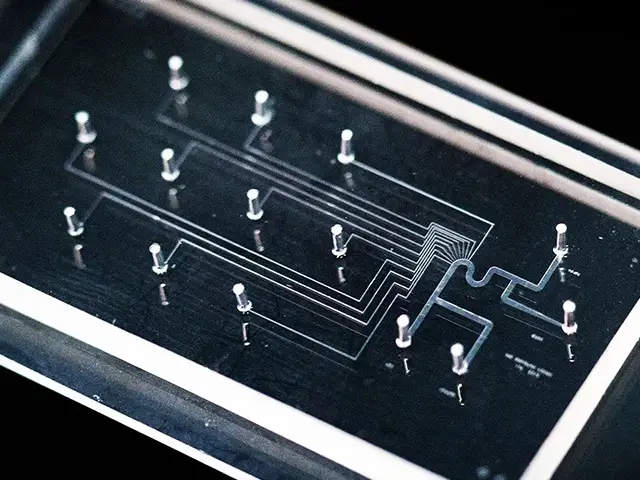
Cold Laser Scribing
This type of scribing uses lasers that emit pulses with extremely short durations (ultrafast lasers) to remove material without heating the surrounding area. It’s ideal for delicate or heat-sensitive materials, ensuring minimal heat-affected zones.
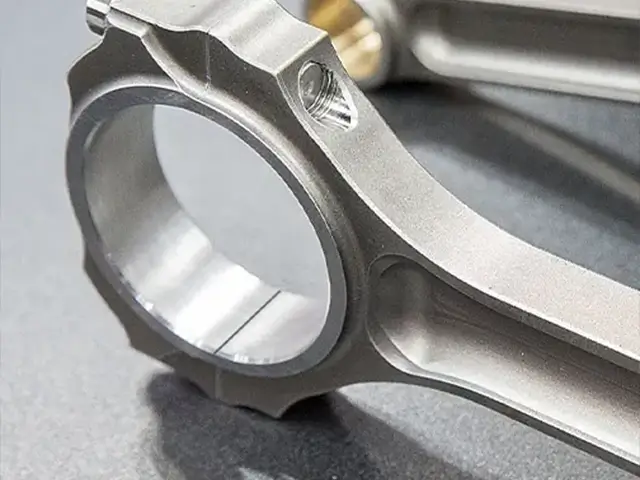

Laser Assisted Mechanical Scribing
This method combines mechanical cutting with laser assistance for improved precision and reduced wear on cutting tools. The laser helps soften or pre-heat the material for easier mechanical scribing.
laser vs alternate
laser Scribing
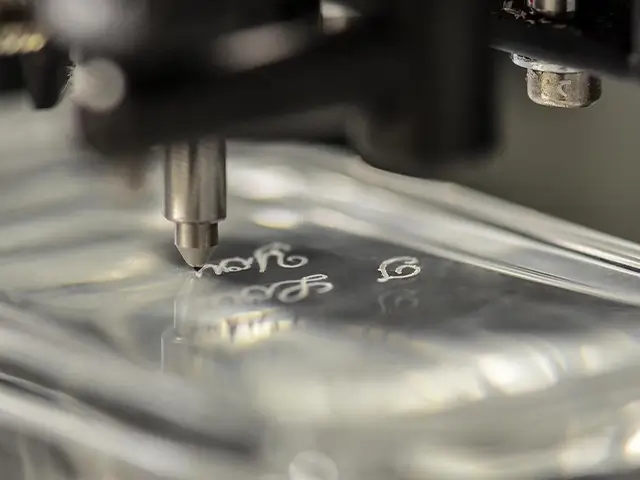

Diamond Scribing

Mechanical Scribing

